

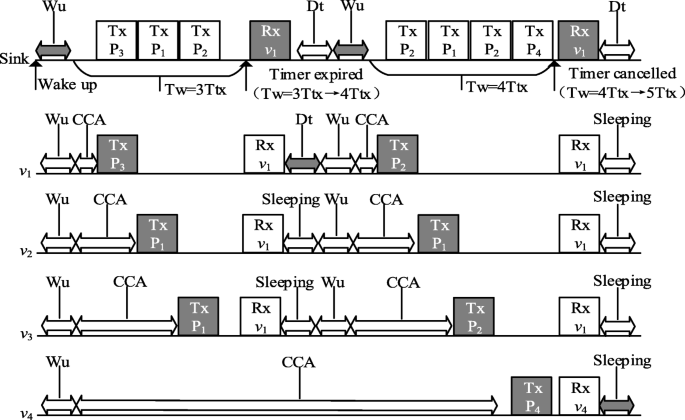
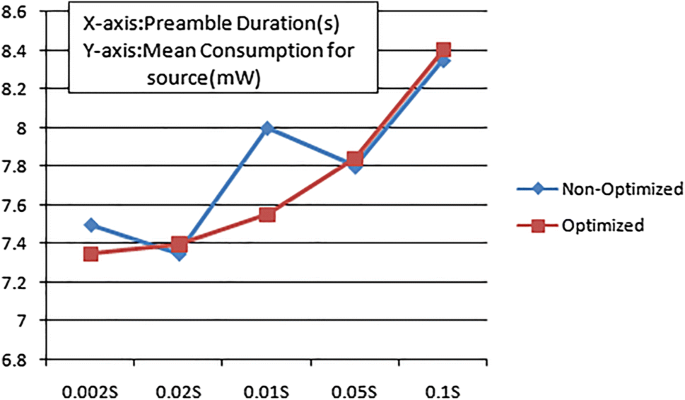
Once aĬontending node senses a channel busy, it initiates a congestionīack-off in order to avoid a collision with an ongoing transmission. To further enhance the performance of the ACK-LPL, we deviseĪnother clever scheme called Short Preamble Counter (SPC). Greatly compared to current ACK-LPL solutions. Listen period), we can increase the transmission success probability Longer than the gap between two consecutive short preambles (i.e., ACK By simplyĮxtending and guaranteeing the CCA duration of the ACK-LPL schemes to be Method called -duration CCA to remedy this problem. Listen period to confirm that the collision problem significantlyĪffects a system performance and then propose a simple yet effective In this paper, we first analyze the collision probability in an ACK
Resolve the collision problem in an ACK listen period. For this reason, it is a challenging task to Induced by an incorrect CCA destroys an ongoing transmission as well asĪ new transmission and results in compromising the benefits of theĪCK-LPL schemes severely. The measured CCA duration (= 128usec) is not enough to avoid collisionsĮffectively in the ACK listen period. As a matter of fact, we measured the CCA duration ofĬurrent commercial sensor motes such as TelosB and found out that Node performs a CCA (Clear Channel Assessment) in the middle of the ACK This situation can be possible if the contending It incorrectly assesses the channel as an idle (indeed busy due to the Of this transmission, a contending node can initiate a transmission if Successfully grabs a channel and initiates a transmission.
Suffers from collisions in an ACK listen period. Briefly, the strobe preamble eliminates overhearingĪnd the early ACK reduces per-hop latency significantly.Įven though the ACK-LPL conserves energy substantially, it still Preamble, only an intended receiver among neighbors immediately replies After sensing and decoding an ongoing short Each short preamble conveys aĭestination address. To remedy this overhearing problem, the ACK-based However, the excessive preamble of basic LPL brings out an Hop neighbors, obliterating tight time synchronizations among sensor Scheme such as B-MAC transmits a long preamble to wake up its one Groups (i) basic LPL and (ii) ACK-based LPL. We can further divide the LPL schemes into two Listening by devising a preamble-based asynchronous rendezvous between a Synchronization among sensor nodes and can be widely utilized in both In contrast, the LPL schemes do not require any time SL approaches fit well in small-sized WSNs in general. Synchronization among all nodes in a network is not a trivial work, the Listening by turning off its radio during the asleep period. Specifying the asleep/awake period for all sensor nodes, and thereby The SL approaches periodically broadcast a control packet Listening (SL) and (ii) low power listening (LPL)
Sensor nodes in the same network are synchronized or not (i) scheduled Duty-cycling approaches areĭivided into the following two categories according to whether the Solutions adopt a duty-cycling mechanism which alternates periodicallyīetween sleep state and active state. To tackle these problems, novel andĭiverse schemes have been proposed. Packet destined for other nodes) problems are two main sources of energyĬonsumption at the MAC layer. Listening for potential packets) and overhearing (i.e., receiving a Most important performance criteria since WSNs consist of numerousīattery-powered sensor devices. In wireless sensor networks (WSNs), energy efficiency is one of the
#Analysis of receiver initiated mac protocol for wireless sensor networks free
MLA style: "Design, analysis and evaluation of a new energy conserving MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks." The Free Library.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
